
Net Zero Carbon Home Update
08/18/2023
The need to lower carbon emissions has driven many industries to find alternative methods to minimize their contribution to a warming planet. The liquid fuel heating industry is no exception to that, and for many decades has been pursuing efficiency and, since the early 2000’s, has been working to develop a renewable and sustainable fuel. The use of renewable biodiesel to replace fossil-derived heating fuels is the most attractive and practical approach at present. Due to NORA research and efforts by manufacturers and fuel marketers alike, the use of higher blends of biodiesel with no. 2 heating oil has increased rapidly over the past few years.
A goal of demonstrating a house that is a net zero emitter of carbon has now been identified by NORA, labeled the Net Zero Carbon Home Project. This can be achieved by substituting the heating fuel with 100% biodiesel (or B100) and installing solar PV to generate renewable, carbon-free electricity for non-heating uses. Since biodiesel is not yet fully carbon neutral, the solar PV system would need to be sized to produce greater energy than what the home requires. The excess carbon-free electricity could then be transferred back to the grid and result in offsetting the small amount of carbon emissions from the biodiesel. A calculator was created by NORA that utilizes a number of parameters such as fuel usage and electricity consumption to calculate how much oversizing of the PV system was required to make the home carbon neutral.
The theoretical groundwork laid down using simple calculations has now allowed NORA to move into the next step: implementation of the theory into an actual home. Currently, NORA is working with various state organizations to find suitable homes for this project. Dr. Thomas Butcher, Director of Research of the NORA laboratory in Plainview, NY, installed solar PV panels in his home, which has been using B100. As of July 2023, this system has been operating with the PV and B100 for a full year. The Table below, which uses the NORA calculator provides a summary of performance and carbon savings over this time.
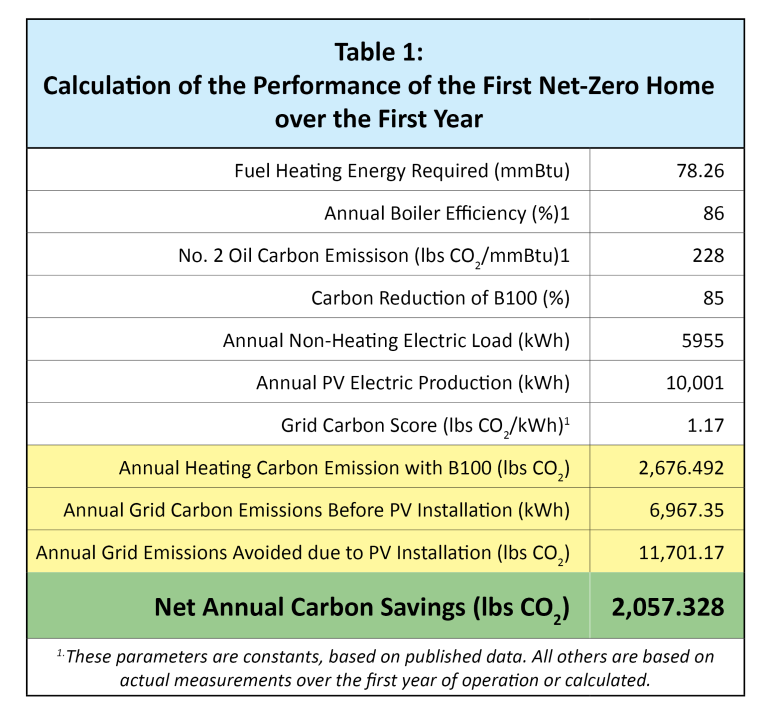
Based on the data and this analysis the Butcher home has been shown to be far better than net zero, actually reducing carbon emissions by over 2,000 lbs during the year relative to the baseline which included use of fossil heating oil. Due in part to lower home electrical power consumption during this year than projected consumption based on usage history. Also, the annual output of the solar PV system was higher than was projected in the pre-installation analysis.
It should be noted that despite a significant air conditioning load in the summer, as shown by the blue bars, each of the summer months contributed to a lowering of the carbon intensity of the grid by producing more energy than was used in the house, as shown by the orange bars.
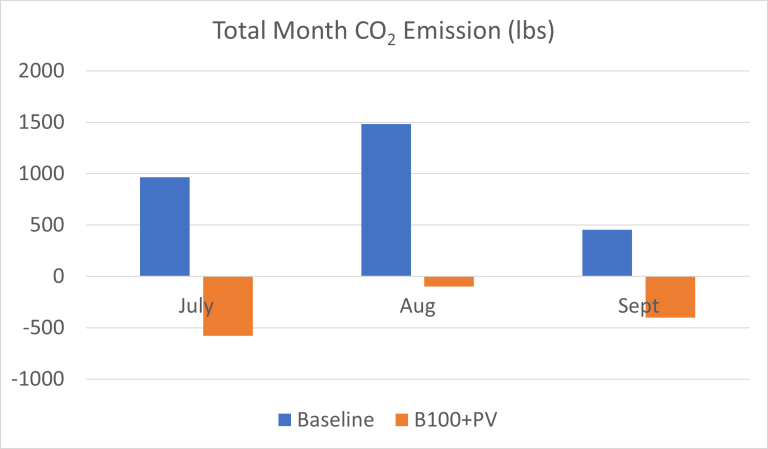
Figure 1: Carbon emission comparison for Butcher home with and without proposed changes (B100 and solar PV)
Bioheated homes in combination with PV present a unique opportunity to lower their greenhouse gas emissions to zero. This is feasible with no public investment and provides a reduction to electricity costs in terms of administrative fees and taxes. This can also minimize the impact on the electrical grid particularly during winter months.
In the case presented here, the homeowner paid for the PV installation minus available state and federal rebates. The payback time for this investment, based on electric power cost savings is estimated at 6.5 years.
